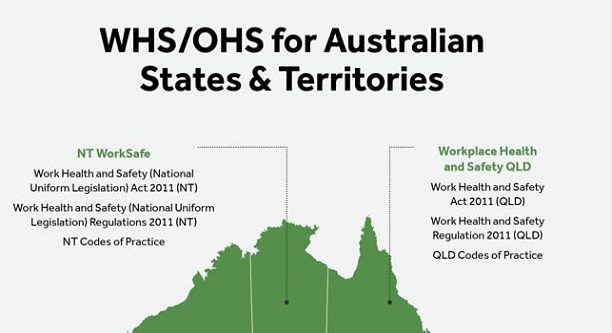
Health and safety law in Australia is governed by a complex system of federal, state, and territory legislation, as well as common law principles. The main components of health and safety law in Australia are designed to ensure that employers provide a safe and healthy workplace for their employees, and that employees are protected from workplace hazards and risks.
The primary piece of federal legislation governing health and safety in the workplace is the Work Health and Safety Act 2011 (Cth). This Act sets out the duties of employers, employees, and other persons in relation to health and safety in the workplace. It establishes a framework for the management of workplace risks, and sets out the process for identifying and addressing workplace hazards.
Under the Act, employers have a duty to provide a safe and healthy work environment for their employees, as far as reasonably practicable. This includes ensuring that equipment, machinery, and other work processes are safe, providing information and training to employees on how to perform their work safely, and implementing measures to manage and control workplace hazards.
Employees also have a duty to take reasonable care for their own health and safety, as well as the health and safety of others who may be affected by their work. This includes following safe work practices, reporting any hazards or incidents to their employer, and using any personal protective equipment provided by their employer.
The Act also establishes the role of the regulator, which is responsible for enforcing health and safety laws in the workplace. The regulator has the power to issue improvement notices, prohibition notices, and fines for breaches of health and safety laws.
In addition to the Work Health and Safety Act, there are also various other federal, state, and territory laws and regulations that govern specific aspects of health and safety in the workplace. These include laws relating to the use of hazardous substances, the handling of dangerous goods, and the management of workplace bullying and harassment.
Employers must also comply with a range of Australian Standards and Codes of Practice that provide guidance on best practice in relation to health and safety in the workplace. These standards cover a wide range of topics, including electrical safety, fire safety, and the safe handling of chemicals and hazardous materials.
One of the key features of health and safety law in Australia is the concept of consultation and cooperation between employers and employees. Employers are required to consult with their employees on health and safety matters, and to provide them with the opportunity to participate in the management of workplace risks.
This consultation and cooperation is facilitated through the establishment of health and safety committees and the appointment of health and safety representatives. These committees and representatives provide a forum for employees to raise health and safety concerns and to work collaboratively with their employer to develop solutions.
In addition to the legal framework, there are also various industry bodies and associations that provide support and guidance on health and safety matters. These include Safe Work Australia, which is responsible for developing national policy and guidance on health and safety in the workplace, and WorkSafe Australia, which is responsible for enforcing health and safety laws in Victoria and Western Australia.
Overall, the main components of health and safety law in Australia are designed to ensure that employers provide a safe and healthy work environment for their employees, and that employees are protected from workplace hazards and risks. By complying with these laws and regulations, employers can help to prevent workplace accidents and injuries, and promote a culture of safety and wellbeing in the workplace.



